Study Guide
Field 165: Music
Recommendation for individuals using a screenreader: please set your punctuation settings to "most."
Sample Selected-Response Questions
Competency 0002
Music Theory
1. Use the graphic below to answer the question that follows.
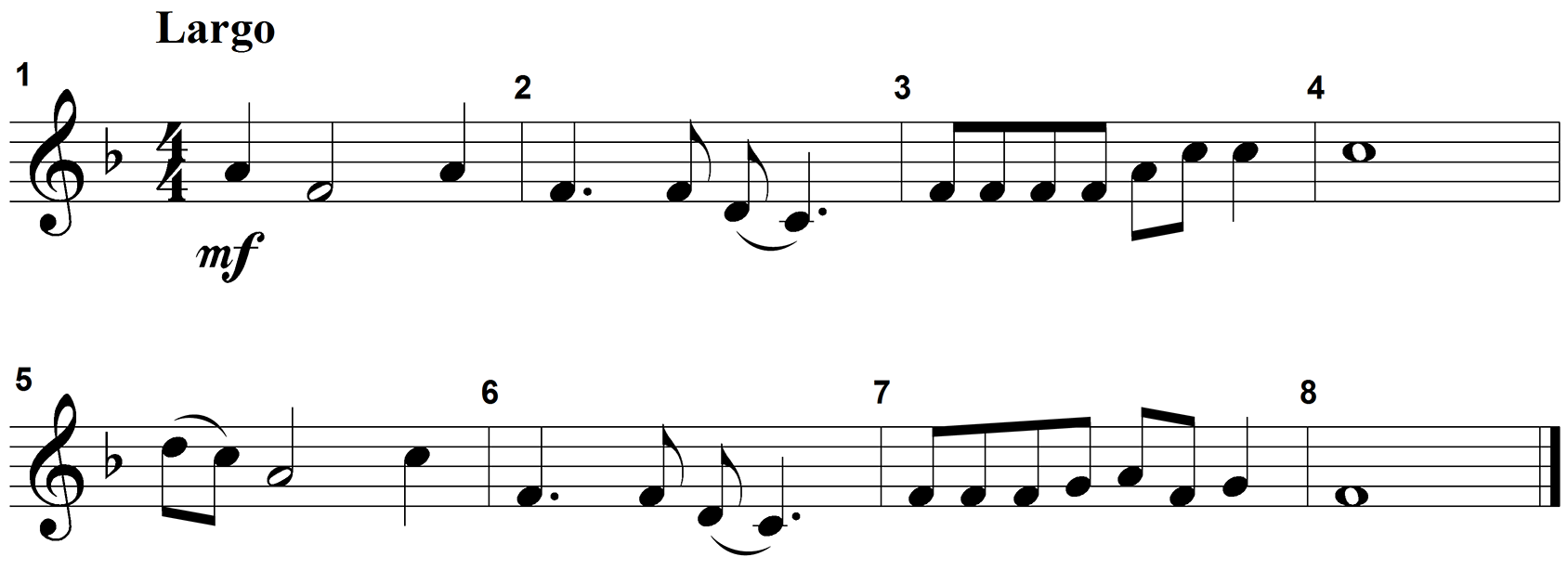
The graphic is a score excerpt. A treble clef appears at the start of the first measure. One flat appears between the treble clef and the 4 over 4 time signature. The tempo marking largo appears above the staff and an mf dynamic marking appears below the staff. The melody is eight measures long and spans an octave from middle C, also known as C4, on the first leger line below the staff to C5 an octave above in the third space. The melody presents the following pitches: measure 1 A, F; measure 2 F, D, C; measure 3 F, A, C; measure 4 C; measure 5 D, C, A, C; measure 6 F, D, C; measure 7 F, G, A, F, G; measure 8 F.
The African American spiritual notated in the excerpt above uses which pitch collection?
- pentatonic scale
- Dorian mode
- blues scale
- Aeolian mode
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. This item requires the candidate to demonstrate understanding of melody, including intervals, pitch collections, motives, form (e.g., periods), embellishments, compositional devices (e.g., fragmentation), and contour. This melody comes to a close on F and uses just five different pitch classes, or note names. They are F, G, A, C, and D. These five notes comprise a typical pentatonic or five-note scale pattern.
Competency 0002
Music Theory
2. Which chord progression exhibits functional tonality?
- Roman numeral 1 – ii – 16 – ii6 – iii6 – 46 – v6 – 1
- Roman numeral 1 – V – ii – vi – iii – vii° – 4 – 1
- Roman numeral 1 – vi – IV7 – 1 – iii – 4 – 7 – 1
- Roman numeral 1 – 4 – vii° – iii – vi – ii – 5 – 1
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. This item requires the candidate to demonstrate understanding of harmony, including tonality, intervals, chord qualities, seventh chords, chromatic chords (e.g., augmented sixths), inversions, chord progressions, conventional voice leading, Roman numeral analysis, cadences, nonchord tones, and treatment of dissonances (e.g., suspensions). Functional tonality is the hierarchy of chord relationships that defines the tonic, or 1 chord, as the resting point or most stable harmony. In this system, a “circle” progression, chords that descend by an interval of a fifth to the tonic, provides the strongest sense of movement toward the tonic. The response option that features descending fifths is D.
Competency 0002
Music Theory
3. Examine the incomplete tone row shown below.
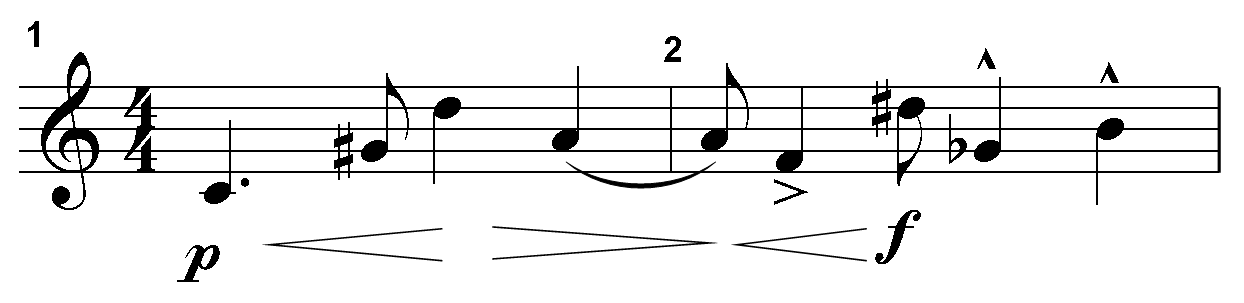
The graphic is a score excerpt. A treble clef appears at the start of the first measure. To the right of the treble clef is a four over four time signature. Under the first measure is a p dynamic marking followed by a pair of hairpin dynamics that become wider then narrower. In measure two an expanding hairpin dynamic leads to an f dynamic mark. Also in measure 2, the second note has an accent mark while the last two notes of the measure have rooftop accents. The first eight pitch classes of this twelve-tone row are C, G-sharp, D, A, F, D-sharp, G-flat, and B.
[On an actual exam, the examinee would see the following directions and would have the ability to click on one of the measures below, drag it to the designated area in the tone row above, and drop it into place. The examinee would be able to change measures until they are satisfied with their choice.]
Drag and drop the correct tetrachord from the measures below into the missing portion of the tone row.
Four measures are shown.
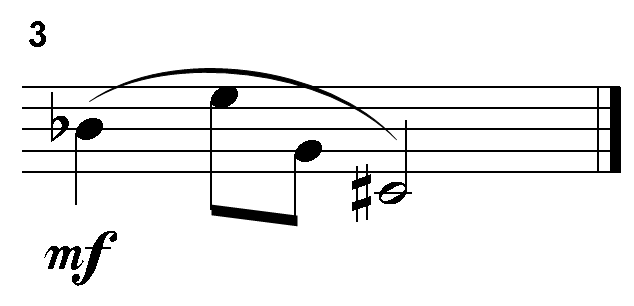 The four pitch classes are: B-flat, E, G, and C-sharp.
The four pitch classes are: B-flat, E, G, and C-sharp.
 The four pitch classes are: C-sharp, G, F, and A.
The four pitch classes are: C-sharp, G, F, and A.
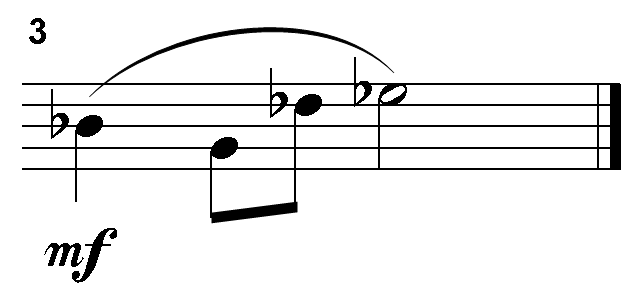 The four pitch classes are: B-flat, G, D-flat, and E-flat.
The four pitch classes are: B-flat, G, D-flat, and E-flat.
 The four pitch classes are: E, B-flat, F-sharp, and D.
The four pitch classes are: E, B-flat, F-sharp, and D.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
-
Correct Response: Top left.
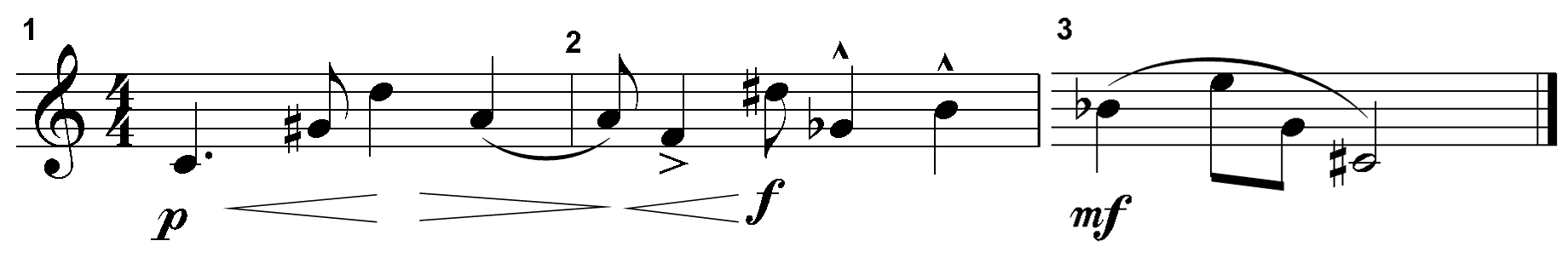
The first two measures are shown again along with measure 3, which has an mf dynamic under it and the pitch classes B-flat, E, G, C-sharp, all of which appear under a slur. The pitch classes of this complete twelve-tone row are C, G-sharp, D, A, F, D-sharp, G-flat, B, B-flat, E, G, and C-sharp.
This item requires the candidate to demonstrate understanding of melody, including intervals, pitch collections, motives, form (e.g., periods), embellishments, compositional devices (e.g., fragmentation), and contour. According to the principles of classical dodecaphonic serialism, a twelve-tone row consists of twelve distinct pitch classes and assumes enharmonic equivalence, which means that C-sharp equals D-flat, D-sharp equals E-flat, etc. A twelve-tone row must first present all twelve different pitch classes exactly once before any other permutation of the tone row can occur. The first eight pitch classes of this tone row are C, G-sharp, D, A, F, D-sharp, G-flat, and B. The tone row lacks the pitch classes C-sharp, E, G, and B-flat or their enharmonic equivalents. The only tetrachord with these four pitch classes is the response option located on the top left side.
Competency 0003
Music Performance
4. Use the graphic below to answer the question that follows.

The graphic is a score excerpt. A bass clef appears at the start of the first measure. To the right of the bass clef are four flats. To the right of the key signature is the letter C. Below the first note is an mf dynamic marking and above it is the tempo marking bluesy quarter note equals one hundred. The melody is four measures long. Measure 1 has three Fs. Measure 2 has E-flat descending to C and again E-flat descending to C, this last note having an accent above it. Measure 3 has B-natural, C, B-natural, C, A-flat, G, and F. The articulation marks above these last three notes are a tenuto mark, rooftop accent, and normal accent. In measure 4, the half-note F is tied from the previous measure.
When sight-singing the melody above according to movable-doe with a doe-based minor, which sequence of syllables is correct?
- la-la-la-sol-mi-sol-mi-ri-mi-ri-mi-doe-ti-la
- doe-doe-doe-ti-sol-ti-sol-fa-sol-fa-sol-mi-re-doe
- fa-fa-fa-me-doe-me-doe-ti-doe-ti-doe-le-sol-fa
- doe-doe-doe-te-sol-te-sol-fi-sol-fi-sol-me-re-doe
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. This item requires the candidate to demonstrate understanding of singing principles, including techniques for developing singing skills, vocal maturation, ranges, diction, sight singing, and strategies for identifying and resolving common singing problems. This excerpt is clearly in F minor as it begins and ends on F and has a key signature of four flats. According to moveable-doe doe-based minor solmization, this tonic F is labeled doe. The excerpt also uses the blues scale in which scale degrees 3 and 7 are lowered compared to their counterparts in the parallel major scale. According to this solmization system, those lowered scale degrees are labeled me and te, respectively. Only response option D begins and ends on doe and uses syllables te and me.
Competency 0003
Music Performance
5. Which Latin percussion instrument is played by scraping it?
- maracas
- güiro
- cabasa
- agogo bells
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. This item requires the candidate to demonstrate understanding of guitar, recorder, ukulele, hand drums, and various other instruments, including types and characteristics, basic playing techniques, instrument maintenance, and strategies for identifying and resolving common performance problems. A güiro is a gourd-shaped, non-pitched percussion instrument that is used in the traditional music of several Latin American countries. To play it, a musician holds the güiro in one hand and uses the other hand to drag a stick across a series of carved notches. This scraping motion across the notches produces the characteristic ratchet-like sound of the güiro.
Competency 0004
Cultural Understanding and Historical Context
6. Which statement best describes Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina's importance in the development of Western music history?
- Palestrina is best remembered today for his role in reforming opera.
- Palestrina's numerous cantatas were inspired by his devout faith.
- Palestrina's music is widely regarded as the pinnacle of sixteenth-century polyphony.
- Palestrina pioneered musical nationalism by incorporating folk rhythms and folk tunes.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. This item requires the candidate to demonstrate understanding of the development of Western music from the medieval era to 17 50, including characteristics (e.g., Renaissance madrigalism) and stylistic performance practices (e.g., Baroque ornamentation); major composers (e.g., Pérotin, Palestrina, J. S. Bach) and genres (e.g., Mass, fugue); ways that music reflects and influences historical developments, cultural factors, and aesthetic values; technological impacts; and contrasts and similarities between music from a variety of musical eras. In Western music history, Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina (15 25 to 94) is best remembered for composing masterpieces that exemplify the late-Renaissance polyphonic style. Primary stylistic characteristics include precise dissonance preparation and descending stepwise resolution; placing dissonances primarily on metrically weak beats, with the exception of suspensions, which occur on metrically strong beats; and balancing an ascending leap with descending stepwise motion in the same voice.
Competency 0004
Cultural Understanding and Historical Context
7. Compared to the Orff approach to music education, the Kodály methodology puts more emphasis on:
- using rhythmic syllables to enhance rhythmic learning.
- using percussion instruments to accompany folk songs.
- performing folk songs to facilitate musical development.
- practicing vocal improvisation to improve sight-singing.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. This item requires the candidate to demonstrate understanding of the purposes of music in society, including settings (e.g., religious), cultural expression, forms of communication, vocations, and avocations; influential music pedagogues (e.g., Orff, Kodály); resources and opportunities to expand musical knowledge and participation; and appropriate audience behavior in various settings. Zoltán Kodály (1882–1967) was an innovative Hungarian music teacher and ethnomusicologist. Typical of many Central European musicians of that era, he was interested in musical nationalism and folk songs, which he notated during field work with the renowned Hungarian composer and folk song collector Béla Bartók. According to the Kodály methodology, students can best develop their musical skills by singing and playing authentic folk songs.